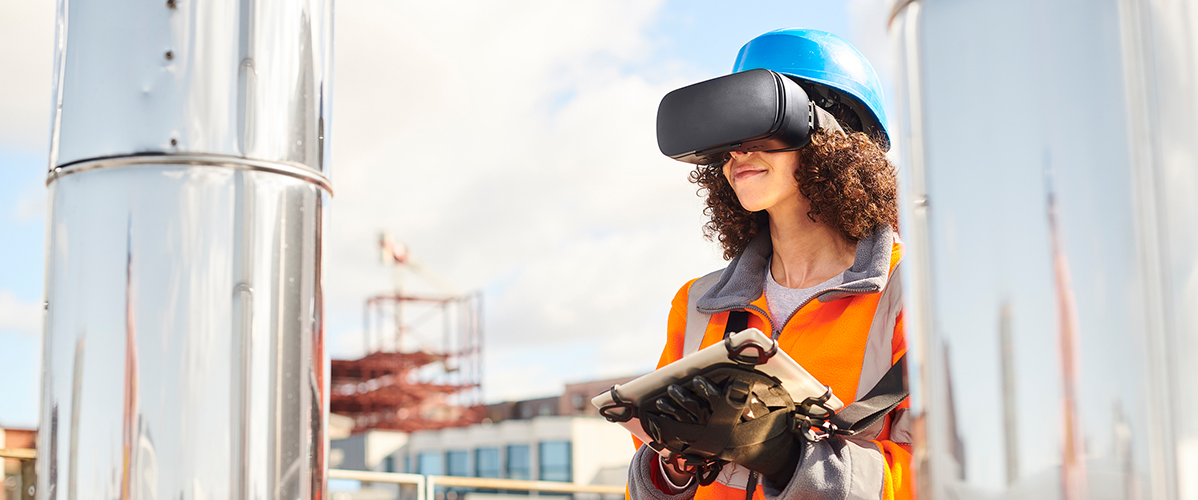
● This emergent approach to reality is being applied in several industries including real estate, video games and education and training.
● According to Precedence Research the XR market is set to grow at an annual rate of 33% to reach 346 billion dollars by 2030.
“XR is a superset integrating the entire spectrum of the virtual-reality continuum”
Training, video games, industry, real estate: numerous sectors are embracing the potential of immersive and semi-immersive technologies collectively known as extended reality (XR). A term that regroups a wide range of environments combining real and virtual elements with various levels of interactivity between them and also with users, XR includes augmented reality (AR), which superimposes 2D and 3D objects on a real environment, virtual reality (VR), which completely immerses users in a virtual universe, and mixed reality (RM), which overlays virtual elements onto a real settings.
The goal of extended reality is to blend the real and virtual worlds to create a new space where people and physical and digital objects can coexist and interact. According to the consultancy Precedence Research, quoted in XR Today, the global XR market, which was worth around 35 billion dollars in 2022, will grow at an annual rate of 33% to reach 346 billion dollars in 2030. This rapid increase is notably linked to the development of remote working in new fields, for example in the health sector, in the wake of the Covid-19 pandemic, Driven by defence and tourism, this market will become more accessible with the massive adoption of 5G and the arrival of new platforms developed by companies like Meta, ByteDance and Engage XR. Designed to take advantage of the low latency and high speeds of 5G, these will deliver higher quality content, which is more immersive and thus more engaging, to users’ mobile devices.
Devices like today’s VR headsets will be enhanced with 3D sound and human-computer interfaces (HCI) which will enable users to control and communicate with systems that will include, for example, location sensors, motion sensors and . XR is therefore a superset that includes the entire spectrum of the reality-virtuality continuum, which extends from the unaltered physical environment to fully immersive virtual reality. Extended reality is already being put to work in several industries. Here are three examples.
Innovative occupational training

Virtual classes, immersive education… Businesses are increasingly turning to XR to create safe and innovative training programmes, which offer students an opportunity to discover professional environments, develop dexterity and technical skills, and master safety procedures. Companies like Engage VR, which recently announced a partnership with Stanford University, are specialising in the development of occupational training tools for the metaverse. XR also has enormous potential for the reproduction of work environments and scenarios, including scenarios marked by risk or situations that are difficult to replicate in the real world, which offer high levels of immersion and interactivity.
The goal is to involve learners in ultra-realist simulations, which develop their understanding of complex systems, and to provide them with exercises designed to prepare them for real world conditions.
Among the companies specialising in this field, GigXR, for example, provides holographic tools for healthcare training. For professions that occasionally have to cope with dangerous working environments (for example, in the energy and construction industries) or with high levels of responsibility (surgeons, aircraft pilots, etc.), XR training offers a means to prepare students for situations with high levels of risk without exposing them to any real danger. At the same time, it also contributes to more effective learning.
Industry 4.0 and virtual design
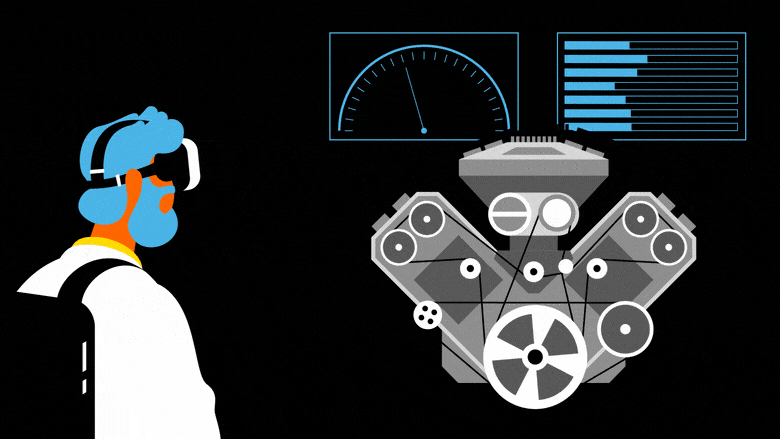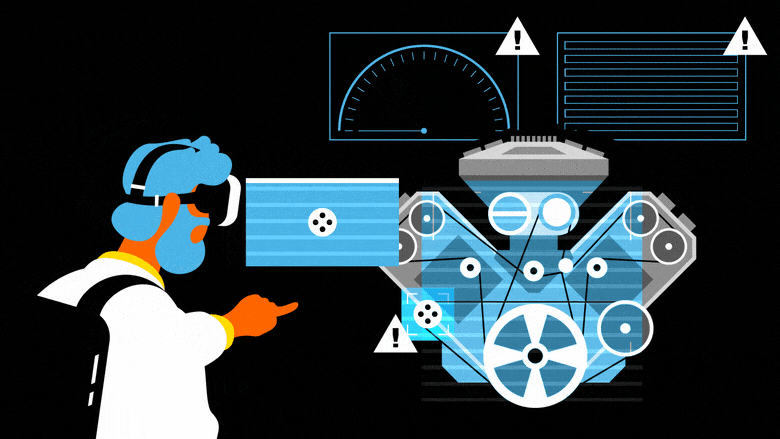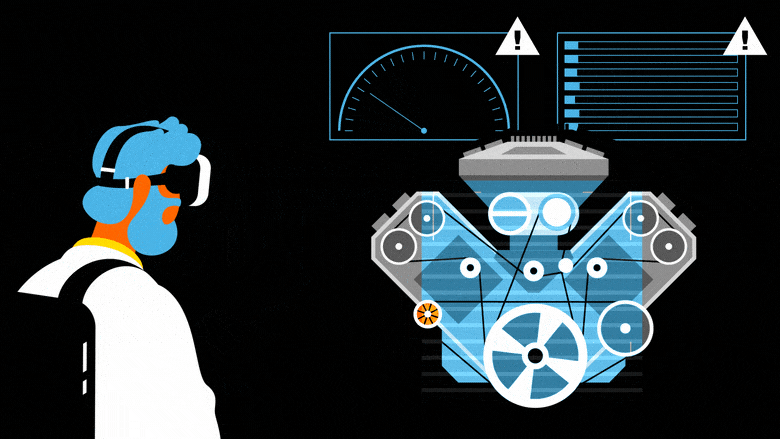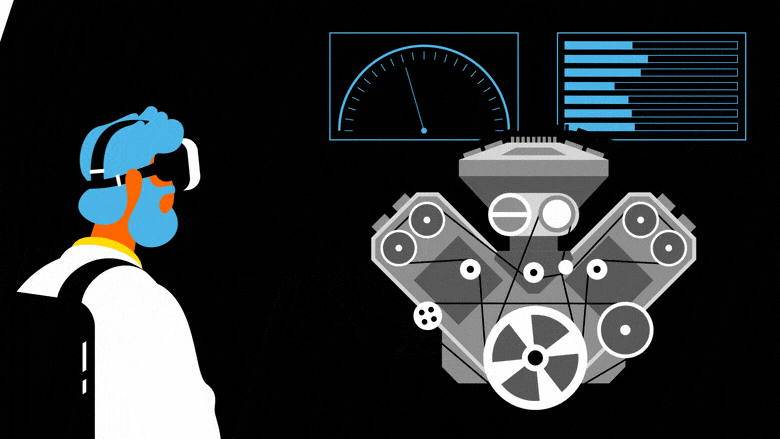
In industry 4.0, XR will feature at every stage of the production process, from research and development to delivery to the market. Companies like Siemens and General Electric have created digital twins of their factories, which can be used to simulate the work of teams and improve productivity. Another application is virtual-reality prototyping, which enables users and teams of users to engage with 3D models of real objects, created with computer assisted design software, while simulating their functioning: an innovation that reduces costs and design lead times, while boosting product quality. Digital twins also enable engineers to rapidly compare the performance of different models and to develop enhanced production processes.
Operator support is a third major industrial application of XR. In particular, mixed reality (MR) can guide operators performing complex tasks with the real-time delivery of contextualized information. For example, when equipped with Hololens headsets, technicians checking the quality of engines can overlay real and virtual parts to evaluate their compliance. They also have the option of accessing digital plans, instructions and recommendations etc.
Virtual real estate visits

In the services sector, real estate agents and developers are taking advantage of XR to convince future buyers. Their goal is to create immersive and interactive experiences to help customers imagine their future properties. Virtual tours give clients an initial idea of multiple properties, which they can immersively explore, before opting to schedule real physical visits. Using AR, future owners, equipped with standard smartphones and tablet computers, can experience the interiors of buildings that are still under construction.
There are also a number of systems that enable potential buyers to fully customize all aspects of their future homes. Real estate agents can now offer customers visiting old houses the opportunity to visualize different layout possibilities. Using mixed reality, future buyers can also experiment with various decorative possibilities, adding furniture in bare rooms and testing different coverings on floors and walls.
Training and education, industrial production and real estate are just some of the fields where these technologies are being deployed. However, the potential of XR is also being explored in several other domains including medicine, e-commerce, advertising, and the cultural industry.