
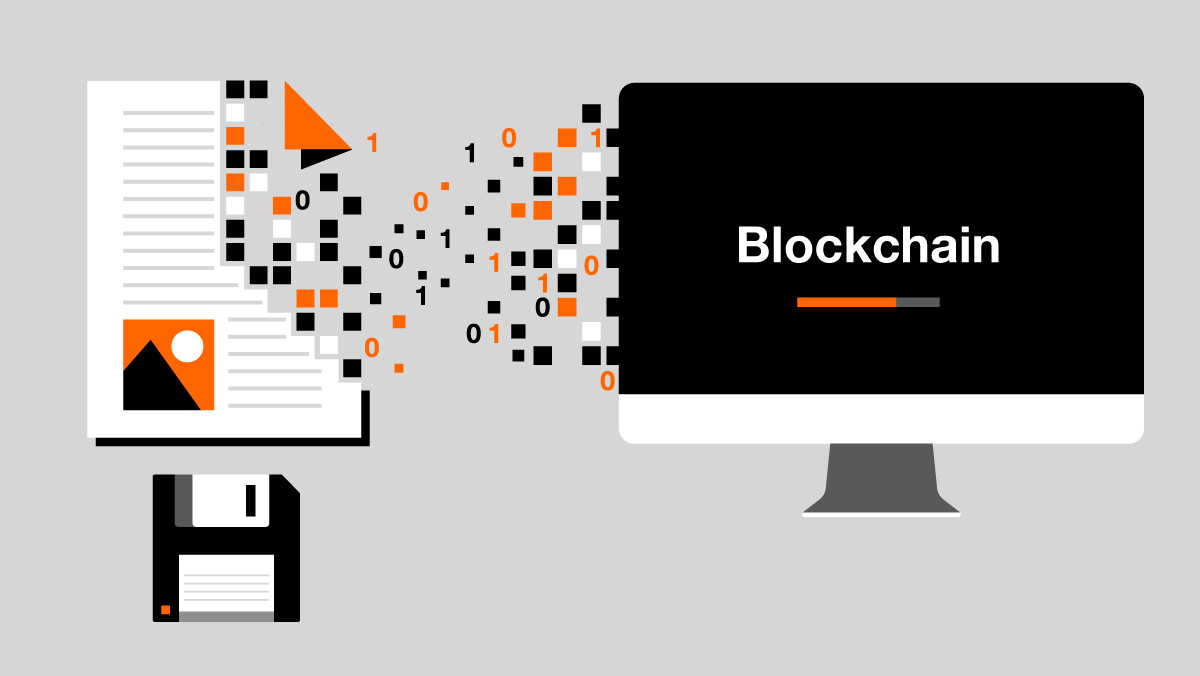
Metadata (title, keywords, dates, etc.) are extracted from the original object and stored in a permissioned Ethereum blockchain platform.
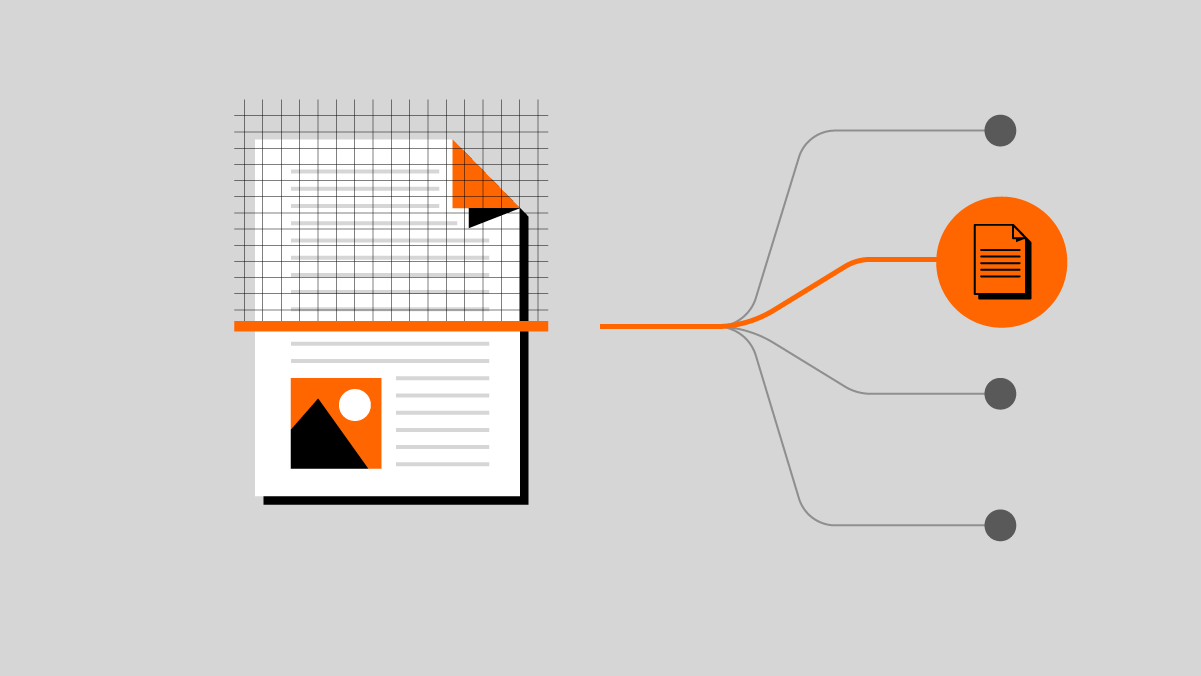
The original object is categorized according to its format thanks DROID (Digital Record Object Identification) software, then run through a hash algorithm that is specific to its format. Hashing is a function that calculates a value that is used to rapidly identify an object.
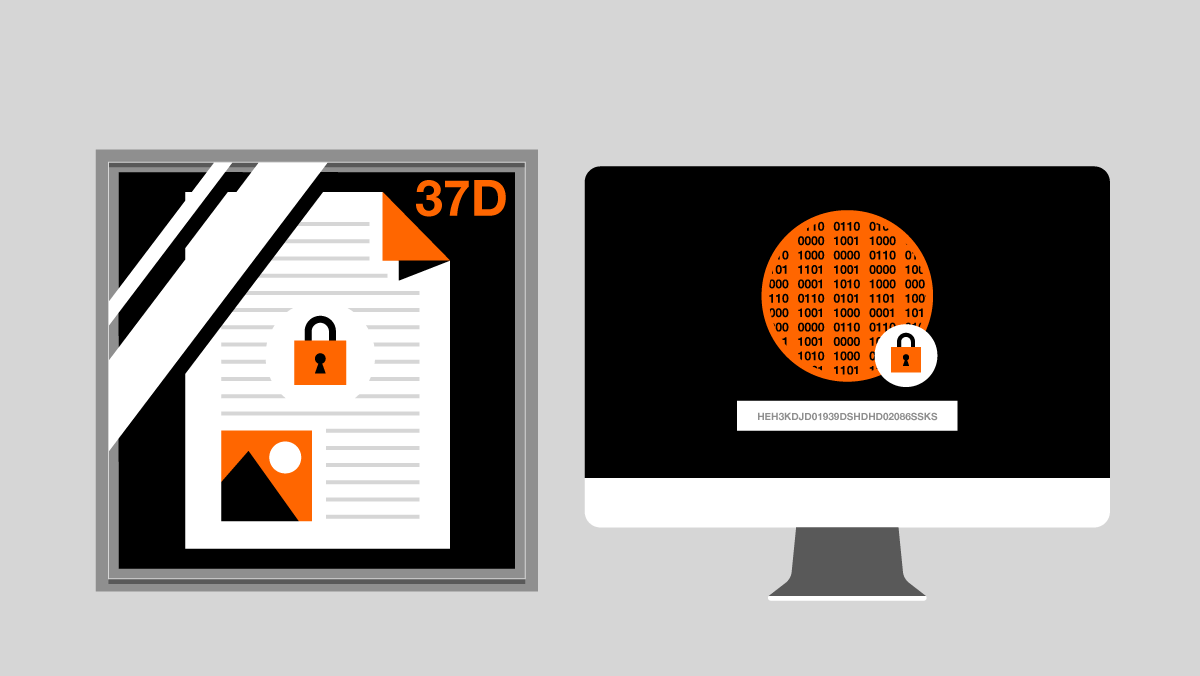
The original object is stored in a secure archive, and its “hash” is stored in the blockchain platform with the metadata taken previously.
When it becomes necessary, the format of the original document is modified. It is then run through a new hash algorithm and the new hash is compared to the original hash stored in the blockchain platform. If they are identical, this means there weren’t any modifications to the object during the change of format.
A research project aiming to use blockchain technology to archive The National Archives’ documents and check their authenticity.










