Artificial pollination: robotic solutions that aim to supplement the work of bees
• In response to dwindling insect populations, engineers are calling on range of new technologies to supplement the work of natural pollinators which have proved to be particularly effective for certain crops, most notably kiwis and tomatoes.
• Developed by a research team led by Yu Gu at West Virginia University, a six-armed robot called Stickbug, which is equipped with a LiDAR system to map its environment and an AI for added accuracy, can efficiently pollinate individual flowers.
• Other research teams are working on alternative robotic solutions, among them an air–liquid spray system to pollinate kiwi flowers. However, to be effective these systems will require the production of large supplies of pollen.
Read the article
• Developed by a research team led by Yu Gu at West Virginia University, a six-armed robot called Stickbug, which is equipped with a LiDAR system to map its environment and an AI for added accuracy, can efficiently pollinate individual flowers.
• Other research teams are working on alternative robotic solutions, among them an air–liquid spray system to pollinate kiwi flowers. However, to be effective these systems will require the production of large supplies of pollen.



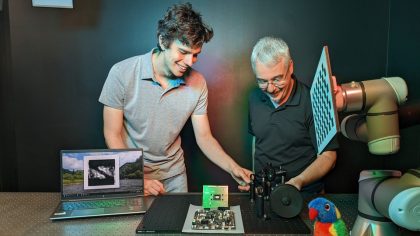
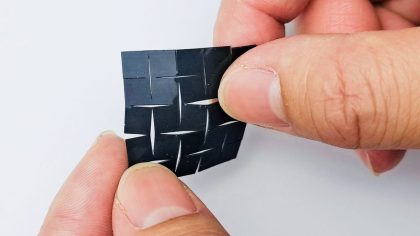
Voice without vocal cords: a machine learning assisted device that enables patients to speak
Read the article
Robots developed by Warwick AgriTech could cut herbicide use by 95%
Read the article
