Smartphone data to map the outer atmosphere and monitor urban wildlife
• A study undertaken by Google Research, in collaboration with leading universities, shows how smartphones equipped with GPS chips can measure the state of the ionosphere, offering unprecedented accuracy in areas with few monitoring stations.
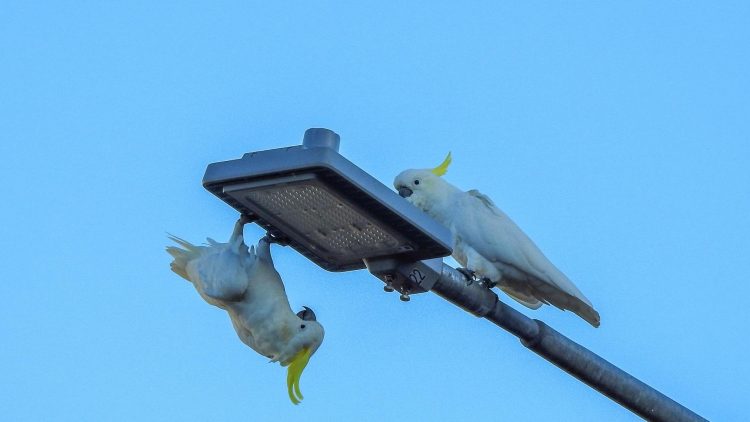
• Studies are also using smartphones to track animals, among them a recent project in Australia, which used low-energy Bluetooth beacons and a crowd-sourced network to monitor the movements of yellow-crested cockatoos.
• The new approach, which respects the privacy of users, only makes use of strictly necessary data. With help from artificial intelligence, it could enable researchers to better understand animal behaviour.
Read the article
• Studies are also using smartphones to track animals, among them a recent project in Australia, which used low-energy Bluetooth beacons and a crowd-sourced network to monitor the movements of yellow-crested cockatoos.
• The new approach, which respects the privacy of users, only makes use of strictly necessary data. With help from artificial intelligence, it could enable researchers to better understand animal behaviour.



Mobile money: an alternative to a bank account for small businesses in Senegal?
Read the article

AI provides a wide range of new tools for historical research
Read the article
Algorithmic biases: neural networks are also influenced by hardware
Read the article
