• Today’s technologies are making insurance more efficient by reducing response times and accelerating the processing of accidents and claims. They are also able to detect fraud in a just a few seconds.
• The transformation will have a major impact on jobs, notably at JP Morgan, which has developed a large language model to take charge of thousands of hours of contract review work.
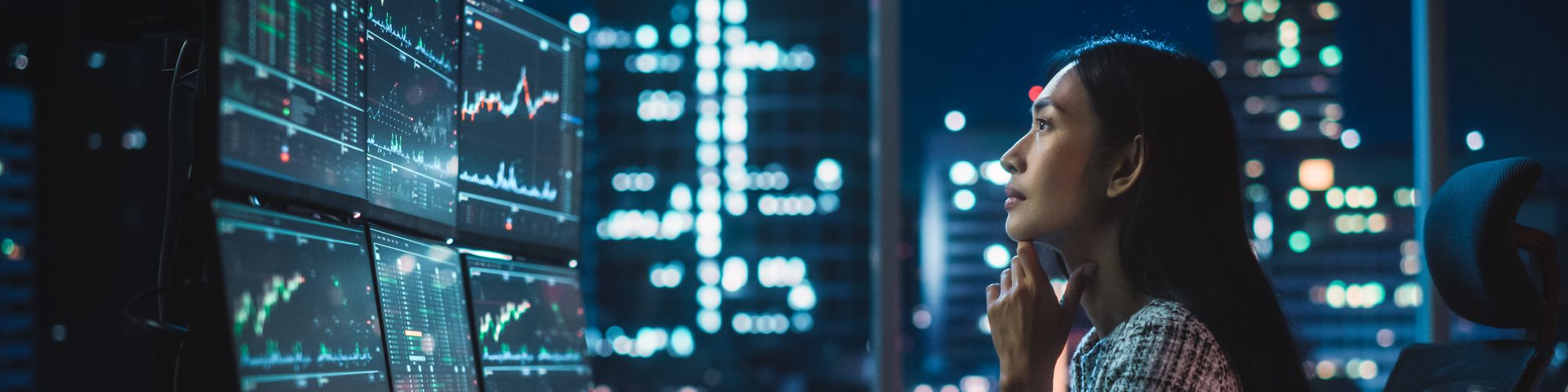
How is AI being used in the world of finance?
In the world of finance, artificial intelligence has been defined as the use of complex statistical tools for diverse applications mainly involving risk measurement, notably techniques such as statistical inference to assess potential exposure to payment default. Over the past decade, progress in AI has been driven by major change in three main areas: firstly, advances in collection and storage have given banks and insurance companies access to large volumes of high-quality and better structured data. Secondly, faster computer processing has enabled them to detect fraudulent credit card transactions in real time. And finally, the mathematical models on which AI depends have been regularly improving from year to year.
JP Morgan has developed an AI to automate tasks that used to consume an annual 360,000 hours of lawyers’ time
How is AI being integrated into financial services, and can you give us some concrete examples?
AI is ubiquitous in the financial sector, and the volume of exchanges it instigates is considerable. For example, on markets: AI systems account for more transactions on the NYSE and Euronext Paris than human traders. In the US, Lemonade has shaken up the world of online insurance, offering an efficient and quick service to subscribers who want to insure their valuables, including personal computers. When you declare a mishap or an accident, Lemonade asks you to make an explanatory video, which will enable their AI system to assess the potential risk of fraud. In barely six seconds, you will receive your insurance payment.
However, such speedy responsiveness comes at a cost. There is a real risk of algorithm bias in processes, which has prompted concerns among academics and professionals. Finally, major insurers are using data from sensors in luxury vehicles to assess the probability of deaths or injuries in accidents. Analysis of this information from cars will also make it possible to tell if garage estimates for repairs are overpriced, ensuring that this technology is used fairly and responsibly.
What about the impact of AI in specific contexts, like the large language model that that went online at JP Morgan in 2023?
In 2021, JP Morgan began development of a dedicated language model, which is specifically trained to review contracts. When it went online in 2023, it was able to take on tasks that used to consume an annual 360,000 hours of lawyers’ time. In addition, the model can assess the reliability of its own conclusions and, if need be, refer them to a human supervisor. Banks are also using AI to identify reasons for losing or accumulating customers, mainly for marketing purposes, which enables them to design campaigns to attract new business.
How is AI affecting jobs in the financial sector, and what are the implications for the future of employment linked to AI?
Although there is no major risk of downsizing as such, it is certain that the world of employment is undergoing radical change. Credit analyst jobs are already disappearing now that AI has moved on from simple to complex and more efficient models. What this means is there will be a shift in the types of jobs that are available. Investment in the training and education of young people is imperative to meet the needs of tomorrow’s industry. AI is being adopted very rapidly, and training will be vital to ensure that these jobs do not move to other parts of the world.
 Jean Dessain
Jean Dessain